Technical SEO is one of the most mysterious parts of SEO even today. Hundreds of ‘Technical SEO Checklist’ is published on different websites and blogs but still many website owners and beginner search engine optimizers are confused about how do these really work?
In reality, having a good onsite SEO checklist right in front of you, will not solve the purpose unless you start implementing those correctly on the websites.
Google keeps us telling that there are “over 200 different ranking factors” and never fully confirms any of those. Therefore, creating a definitive technical SEO guide is next to impossible.
This technical SEO guide covers the six most important factors which should be taken care of with utmost attention and 100% precision.
The technical SEO parameters everyone needs to follow.
Here are the top six things that need to be always on your to-do technical SEO checklist.
1. Sitemaps
If you want to build a strong and structurally correct technical optimization and SEO foundation, take your website’s sitemap files into account, both HTML and XML versions.
Having a properly formatted XML Sitemap makes sure that you kept all important internal URLs of the website listed at one place for the search engines.
The HTML Sitemap is just a well-designed table of internal URLs of the entire website that human users can use to browse through the right pages quickly. While this has no direct SEO impacts, Search Engines reward websites that offer a good user experience.
Do we really need sitemap files today? This can be a valid question. Because long back Google used to use sitemap.xml to understand the internal URL structure of a website for its crawling purpose. But with advanced technologies today Google is more than capable of identifying the URLs of a website without the help of its sitemap files.
So what’s the point of keeping sitemap files of a website? Here is why Sitemaps are still one of the top onsite SEO factors.
- Helping search engines to crawl and index one website and its web pages is a good practice. Even if we don’t put sitemap files, still search engines can easily find out pages of a website from different internal and external sources. But keeping a sitemap file will make this process much easier for search engines.
- Google still has a sitemap section on its Search Console tool. Therefore, not only keeping but adding and resubmitting sitemap files to the webmaster tools like Google Search Console will make the crawling even quicker and better.
- On a site’s robots.txt file we use to put the absolute URL of the website’s sitemap file. Hence keeping the sitemap file is still relevant.
For CMS users, there are lots of good plugins available to generate Sitemaps. For comparatively smaller Non-CMS HTML or PHP websites, there are many one-click Sitemap generators available online. For big websites, portals and eCommerce platforms there should be an internal mechanism to develop and update sitemap files regularly.
2. Robots.txt file
Robots.txt file is very crucial for the website’s technical SEO and search engines. This file doesn’t have anything to do with a regular human visitor of the site. It is exclusively created for and used by the major search engines.
One robots file accomplishes 3 primary things.
- One robots file may list search engines which are not allowed to crawl the website.
Example:
User-agent: example-search-bot
Disallow: / - One robots file may list all the directories of the site, which are not to be crawled by any search engines.
Example:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /directory/ - One robots file may list all the URLs of the website, which are not to be crawled by any search engines.
Example:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /page.html
Why do we need to block a search engine from crawling a website? There can be several reasons for this. One such reason is, maybe the website is live on the internet but under development.
And we may not want that under construction site with dummy contents to be crawled and indexed by the major search engines. There can be other reasons as well for blocking search engines using the robots.txt file.
Similarly, one website may have few sections or pages which we don’t want to rank on search engines for good reasons. Hence we have to block those directories and URLs using robots file.
There are two important things to remember here:
One, never ever blocks any webpage or other resources unnecessarily from search engines. This can even damage one site’s organic ranking potentially.
Second, the robots.txt file doesn’t guarantee anything. This means, if search engines find any external sources to crawl a webpage, it will crawl and may index that page even if it is blocked from the robots.txt. Though in that case, the description tag won’t appear on the search results.
So, what if we do not want one page to rank? How to block, if the robots file doesn’t guarantee its blocking? We need to block its indexing by putting <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex” /> in the head section of that page.
At times we may create multiple same intent landing pages with different offerings and discounts mainly for the paid marketing (Google Ads, Facebook marketing etc.). These landing pages contain substantially same content which is already published on a webpage that meant to rank organically.
This can create significant organic ranking problems for that original content page. In this case, blocking those landing pages’ organic indexing will eradicate the issue.
Additionally, we should mention the XML sitemap paths at the bottom of the robots.txt file.
Example:
Sitemap: http://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
3. Canonical tags
The ‘canonical’ tag can resolve the duplicate content issue very quickly by telling Search Engines which version of the URL to index for one content.
Sometime, one content may open on multiple URLs of a website. This happens frequently if we use CMS. Besides, if we use URL re-writing technique, one page may open on two URLs. This makes it difficult for Google and other search engines to identify the exact version of the URL we want to index and rank on search engines.
In some other cases, we may want to publish one content on a website which is already published somewhere else. All these will create duplicate content issues which can bring problems to the website.
Canonical URL solves this issue by mentioning the one URL which we want search engines to index, as the canonical URL on each webpage’s head section. Search engines will consider the canonical version of URL as the correct URL to index, and rest all URL versions for that same content will be ignored.
Therefore if you are republishing a content which is already up and live somewhere else, then you must refer the original content page URL as the canonical URL on the duplicate content page’s head section.
<link rel=”canonical” href=”original content page URL” />
The benefits of using the canonical URL:
- Solves the duplicate content issues.
- Helps search engines to identify the right URL to index.
- Improves the ranking of the original content.
4. Proper redirection
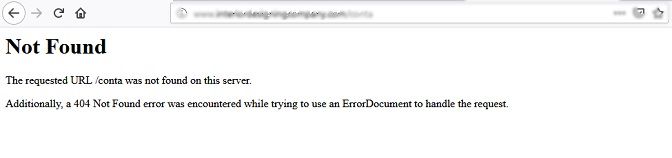
Redirection is another important thing which we may need to do frequently as and when we get ‘404 error page’ information, or if we ourselves want to move from one URL to another URL for some reasons.
If we encounter ‘404 error’ on a page, that will lead to a default blank browser page (if no custom error page is designed). Excessive of this will cause a major user-experience problem which can even harm site’s indexing and eventually the organic ranking.
And sometime we may also need to redirect our visitors from one URL to another URL due to some reasons. In both these cases, redirection is the solution.
There are mainly two types of redirections. One is the permanent redirection, which is called ‘301 redirection’. And the second is the temporary redirection which is ‘302 redirection’.
The uses of these two types of redirections have completely two different purposes.
In a situation when we want to move from one URL to another URL permanently, we need the ‘301 redirection’. This happens mostly because of the changes are done on an existing page URL permanently, or may happen due to the removal of one page permanently.
The ‘301 redirection’ tells search engines that we moved from the old (or non-existing) URL to the new (or existing) URL permanently. As a result search engines will de-index the old URL and start indexing the new URL while transferring most of the PR (Page Rank) juice from the old URL to the new URL.
Redirect 301 /services.html https://www.example.com/seo-services.html
We need the ‘302 redirection’ in cases where we are shifting from one URL to another URL for a particular time being and not permanently. If your website is under maintenance, you may want to show one custom maintenance message to your site’s visitors.
In this case, you need to redirect your website’s traffic to one custom designed page. This is when you need the ‘302 redirection’. Once the maintenance is over the website will be restored to its previous state. There will be no PR transfer in case of a ‘302 redirection’.
Redirect 302 /services.html https://www.example.com/maintenance-page.html
5. Custom error pages
If you have a huge website, then it is quite likely that you frequently encounter 404 error pages. You may get this 404 error page information on your Google Search Console account or if you analyze your website using tools like ‘Small SEO Tool’ to check its 404 pages.
This happens mainly because of the three reasons:
First, you might have deleted one page earlier but that deleted page URL is still there on the internet. Now when a person clicks on that URL, they are landing on a non-existing page.
Second, one URL might have been changed but the old version of that URL is on the internet without a redirection. When it is clicked by users, they are taken to a non-existing page.
Third, one internal, or inbound link is built by mistake with a wrong hyperlink path. This will also lead all its visitors to a non-existing page.
In all these cases the solution is the proper redirection. But you can redirect the non-existing URL to an existing, internal, relevant URL only when you have that information. But what if there are a few 404 error pages which you haven’t seen yet? Aren’t those leading all visitors to a blank page? Yes, visitors who are clicking on those non-existing links are visiting a page with a default browser message of ‘requested URL was not found’ or similar.
If you think, what the big deal with this, you are making a big mistake indeed. This can cause several issues with your website’s optimization and sales as well.
When someone is clicking on a link with the purpose of purchasing something from your website and finally landing on a default 404 error page, they don’t have anything to do other than going out of the site. This will not only increase the website’s bounce rate but may also increase the Pogo-sticking which is a real negative signal for the website in front of Google. Improving this situation will retain those visitors on your website, hence will decrease the bounce rate, pogo-sticking, and increase the sales.
But how will you correct it unless you have the information of those 404 error pages? This is where a custom error page comes in handy. In this process, we need to design a couple of custom error pages for a few common errors, like, 404 (page not found), 403 (forbidden) etc.
Along with this, we use the htaccess file to direct all those visitors about to visit the default blank error pages to the custom designed error pages. Example:
ErrorDocument 404 /errorpage404
These custom error pages are to be designed in a way that all visitors get enough relevant options to browse through the website even if they don’t land on the page they wished to.
The benefits of Custom Error Pages:
- This reduces the bounce rate and pogo-sticking of the website.
- This increases site’s page-views and dwelling time.
- It impacts on sales numbers.
- This enhances user-experience, which indirectly improves the organic rankings.
6. Preferred domain version
Preferred domain version has to be set even before you launch your website.
Consider these – example.com, www.example.com, example.com/index.html, www. example.com/index.html. Do all of these links lead your visitors to the same content? Yes, and of course your website is in trouble.
You need to fix this problem ASAP. This should not create any problem for human visitors but this will cause major issues for the search bots. Search crawlers will consider these four URLs as four different websites or links with the same content.
Setting up a preferred domain will solve this issue. We need to set only the one version of these four as our preferred domain (preferably www.example.com). Rest of the domain versions should redirect themselves permanently to the set version.
If you have a WordPress website, you can set the domain version from the WordPress settings. In case you have a website which is not on WordPress, you can set the domain version using website’s htaccess file.
Non-www to www
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^(?!www\.)(.+) [NC]
RewriteRule ^(.*) http://www.%1/$1 [R=301,NE,L]
www to non-www
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www\.example\.com [NC]
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ http://example.com/$1 [L,R=301]
In the rarest situation, where you neither have any access to the site’s wp-admin (for WordPress websites) nor the htaccess file, you can set the preferred domain using Google Search Console tool.
Wrapping things up
Technical SEO is meant to build a solid architectural foundation of the website which will help search engines to crawl and index its pages easily and correctly. If we can perfect these 6 technical SEO attributes, we may instantly experience a lot of improvements to the site’s organic ranking. These 6 are the most essentials but there are other technical SEO parameters which need to be taken care of as well.
Author Bio:
Soumya Roy is the Founder & CEO of PromozSEO Web Marketing Academy. He is a veteran digital marketer and search engine specialist with over 11 years of experience. Soumya is also the lead SEO & internet marketing trainer at PromozSEO.com. He enjoys writing contents on topics related to digital marketing, search engine optimization, paid ad marketing, social media marketing, user-experience, business-branding and many more.